Content
Learning objective number 6 is to prepare adjusting entries to accrue uncollected revenue. The adjusting journal entry required on May 31st is to debit, or increase, Depreciation Expense on Equipment and credit, or increase, the account Accumulated Depreciation on Equipment for $50. Here is the entry made by Webb on January 1st to record the purchase of the policy. A debit, or increase, is made to the asset Unexpired Insurance, and a credit, or decrease, is made to the asset account Cash for $2,400. On subscription, the issuer of bonds with bond warrants records in account 487 the difference between the issue price of the bonds with bond warrants and the current value of the debenture loan. When the warrants are exercised, the deferred income is recorded in the profit or loss over the term of the loan. When the warrants expire, the amount of unexercised warrants is recorded in the profit or loss.
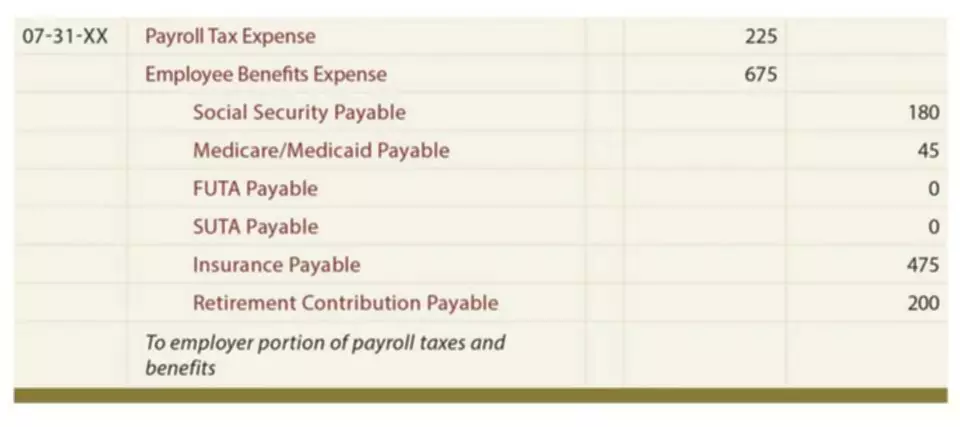
- Under the expense recognition principles of accrual accounting, expenses are recorded in the period in which they were incurred and not paid.
- Accruals leads to a decrease in costs and increase in revenues.
- During March they fixed a computer, but the customer not picked it up or paid by the end of the month.
- Accruals and deferrals are instrumental in helping this proper reporting of revenues and expenses happen.
- She is a CPA, CFE, Chair of the Illinois CPA Society Individual Tax Committee, and was recognized as one of Practice Ignition’s Top 50 women in accounting.
- For example, if you pay $6,000 for six months of rent upfront, you put the $6,000 into a deferred expense account and debit the account $1,000 each month for six months.
- C) The account balance is needed in determining the book value of the related asset.
It arises when an entity makes a payment for goods or services in advance of receiving them. An example is when a renter pays their quarterly rent payments in advance. A corporation must pay income tax on its taxable income. Corporate taxes are due on March 15th of the year following the year in which the income was earned.
Why defer expenses and revenue?
But the thing with accruals is that you don’t have to wait for the involvement of cash for you to record transactions. However, the cash accounting method does not conform https://www.bookstime.com/ to the US GAAP or the IFRS. Unearned revenue is money received by an individual or company for a service or product that has yet to be provided or delivered.
Since you still have to earn the revenue, you need to defer it even if you already received the payment. And for cash disbursements, you will record an expense. This is to represent the fact that you’ll be parting with cash sometime in the future. This is to represent the fact that you will be receiving cash sometime in the future.
Accrual vs Deferral – Meaning and Differences
Accrued ExpensesAn accrued expense is the expenses which is incurred by the company over one accounting period but not paid in the same accounting period. In the books of accounts it is recorded in a way that the expense account is debited and the accrued expense accruals and deferrals account is credited. A deferral of revenues or a revenue deferral involves money that was received in advance of earning it. An example is the insurance company receiving money in December for providing insurance protection for the next six months.
- The evidence is compelling in favor of accrual accounting, and it is consistent with what we observe when we see analysts predominantly forecasting earnings rather than cash flows.
- The journal entry for deferred revenue is Revenue account debit and Deferred revenue account credit.
- Adjustment entries with a time lag in the reporting and realization of income and expense.
- Accrual is a very important method to reflect the true position of the company, however, the cash statement also has its importance as it tells about the ability of the company to generate cash in the business.
- For the fiscal year 2022 close, we will follow the schedule listed below for all expenses.
- Deferrals are all about timing, within the context of earning revenue and matching expenses.

